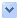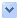圖1. Rhytidophyllum auriculatum(一種加勒比海伊斯帕尼奧拉島特有的苦苣苔科種植物)與Rhytidophyllum vernicosum(原產於加勒比海島嶼及南美洲北部的苦苣苔科種植物)雜交的3D圖像。 (圖援用自原文)
3D image of a hybridization between Rhytidophyllum auriculatum and Rhytidophyllum vernicosum.
A team of researchers has created 3D models in order to gain a better understanding of the evolution of flowers.
為了獲得更深入瞭解花的演進,一支研究人員團隊已經創建了3D模型。
A team of researchers from Montreal, including those from McGill University, the University of Montréal, and the Montreal Botanical Garden, are using photogrammetry – a technique commonly used to reconstruct landscape topography – to gain insights into the evolution of flowers.
一支來自加拿大蒙特利爾市,包括那些來自麥吉爾大學、蒙特利爾大學及蒙特利爾植物園的研究人員團隊,正在使用攝影測量法(一種常用於重建景觀地形的技術),來獲得花演化的洞察力。
This is the first time that photogrammetry has been used in the study of flowers, the results of which have been published in the journal New Phytologist.
這是首次,攝影測量法被使用於花的研究。其成果,已被發表於《新植物學家》期刊。
Photogrammetry uses information gathered from photos taken from different angles. Thanks to the triangulation of common points present in the photos, it’s possible to reconstruct a 3D model of a flower. Colors are then applied to the 3D flower using information from the photos.
攝影測量法使用,從不同角度拍攝之照片收集的資訊。由於,照片中存在之共同點的三角測量,重建花的3D模型,這是可能的。然後,使用來自照片的資訊,將顏色施加於此3D花上。
According to the researchers, photogrammetry has the potential to boost research on flower evolution and ecology by providing a simple way to access three-dimensional morphological data. Databases of flowers – or even of complete plants – could give scientists and the public a way to finally see the unique features of plant species that remained hidden from view.
根據研究人員們的說法,攝影測量法具有,藉由提供一種,取得三維形態數據的簡單方法,來增強針對花演化及生態之研究的潛力。花(甚至屬完整植物)的數據庫,能為科學家及公眾們提供一種,最終看到,依然躲開觀察之植物物種特徵的方法。
“The variety of shapes and colors seen in the plant world are difficult to capture with simple photography. That’s why I became interested in adapting technological tools to capture the form of flowers,” says McGill University professor Daniel Schoen, who first had the idea of applying photogrammetry to flowers, while doing research at the Institut de recherche en biologie végétale.
在蒙特利爾植物生物學研究所(the Institut de recherche en biologie végétale)進行研究時,最早懷有將攝影測量法應用於花之構想的麥吉爾大學教授,Daniel Schoen宣稱:「於植物世界中,被看見之形狀及顏色的多樣性,很難使用簡單的攝影術來捕捉。那是為何我變得感興趣於,採用技術工具,來捕捉花的形態。」
“Understanding floral evolution is important because flowers are the principal drivers of plant diversification through speciation, a major determinant of plant biodiversity,” says Professor Schoen.
Schoen教授宣稱:「瞭解花的演化很重要。因為,花是透過物種形成(植物生物多樣性的一種主要決定因素)之植物多樣化的主要驅動物。」
“Together, the team developed something we think will help advance our understanding of how flowers diversify in response to their interaction with pollinators. Thanks to our 3D models, it’s possible to admire flowers from every angle,” he says.
他宣稱:「同時,該團隊開發了,我們認為將有助於提升,瞭解有關花,在對其與傳粉媒介之交互作用作出反應時,如何多樣化的東西。由於我們的3D模型,從每一角度欣賞花,這是可能的。」
Flowers are complex and extremely varied three-dimensional structures. Capturing their forms is important to understanding their development and evolution. 91 percent of flowering plants interact with pollinators to ensure their reproduction in a 3D environment.
花是複雜且極度多變化的三維結構物。捕捉它們的形態,對於理解它們的發展及演化很重要。91%的開花植物與傳粉媒介交互作用,以確保它們在 3D環境中的繁殖。
The morphology and colors of the flowers act like magnets on pollinators to attract them. Yet the 3D structure of flowers is rarely studied, the researchers explain.
花的形態及顏色對傳粉媒介,起如同磁鐵般吸引它們的作用。不過,研究人員們解釋,花的3D結構很少被研究。
The use of photogrammetry has real advantages compared to other existing methods, in particular X-ray microtomography, which is by far the most widely used method to build 3D flower models, say the researchers.
此些研究人員表示,與其他現有方法相較下,攝影測量法的使用,具有名符其實的優勢。特別是,迄今最廣泛被使用,來構建花3D模型之方法的X-射線顯微斷層攝影術。
“Photogrammetry is much more accessible, since it’s cheap, requires little specialized equipment, and can even be used directly in nature,” says Marion Leménager, a doctoral student in biological sciences at Université de Montréal and lead author of the study. “In addition, photogrammetry has the advantage of reproducing the colors of flowers, which is not possible with methods using X-rays.”
該項研究首要撰文人,加拿大蒙特利爾大學,生物科學方面的博士生,Marion Leménager宣稱:「攝影測量法的取得較容易得多,因為它便宜,僅需少許專門設備,且甚至能直接被使用於自然界。此外,攝影測量法具有,使用X-射線方法所不可能之再現花顏色的優勢。」
The first results, although imperfect, were enough to convince Leménager to devote a chapter of her thesis to it. “The method is not perfected yet,” she says. “Some parts of the flowers remain difficult to reconstruct in 3D, such as reflective, translucent or very hairy surfaces.”
雖然不完美,不過此些最初的研究結果,足以使Leménager將其論文的一章,專用於攝影測量法。她宣稱:「此方法尚不完善。於3D中,花的某些部分仍難以重建,諸如反光、半透明或非常多毛的表面。」
“We have shown that photogrammetry works at least as well as more complicated and expensive X-ray methods for visible flower structures,” says University of Montréal professor Simon Joly, who conducts research at the Botanical Garden.
於蒙特利爾植物園進行研究的蒙特利爾大學教授,Simon Joly宣稱:「我們已經證實,就可見的花結構而言,攝影測量法至少與較複雜且昂貴的X- 射線法一樣有效。
“Thanks to the living collections of the Montreal Botanical Garden, our study of plants from the Gesneriaceae family, like the African violet, demonstrates that 3D models produced using this technique allow us to explore a large number of questions about the evolution of flowers.”
多虧加拿大蒙特利爾植物園的現存收集,我們來自諸如非洲紫羅蘭等,苦苣苔科植物的研究證實,使用該種技術產生的3D模型,使我們得以探索,有關花演化的大量問題。」
網址:https://scitechdaily.com/the-hidden-secrets-of-flowers-understanding-floral-evolution/
翻譯:許東榮
文章定位: